Types of Epilepsy Seizures
Reviewed by: HU Medical Review Board | Last reviewed: November 2021 | Last updated: April 2025
People often use the words "epilepsy" and "seizure" to mean the same thing. However, a seizure is an event. Epilepsy is a disease in which a person has repeated seizures.
Epilepsy is a neurological (brain) disease. With epilepsy, nerves in the brain do not work properly and cause repeated seizures. A person having a seizure may do many things, such as:1,2
- Stare or seem to daydream
- Look or act confused
- Shake or twitch
- Fall
- Lose consciousness
There are 2 major types of epilepsy: generalized and focal. Generalized and focal describe the different kinds of electrical activity in the brain that cause seizures.1,2
Generalized epilepsy is caused by abnormal electrical activity on both sides of the brain at the same time. Focal epilepsy is caused by abnormal electrical activity in only 1 part of the brain.1,2
What are the 2 major types of seizures with epilepsy?
Within these 2 main types, there are many different names that describe the kinds of epilepsy. These terms are used to describe seizures more precisely:1,2
- Myoclonic– These seizures cause occasional, brief jerking, usually on both sides of the body. The person usually does not lose consciousness.
- Clonic– These seizures cause repeated jerking in a rhythm on both sides of the body, including the face and neck.
- Tonic– These seizures cause muscle stiffness. The person usually loses consciousness.
- Atonic– These seizures cause muscles to relax, especially in the legs. These may also be known as drop attacks since the person often falls to the ground if standing.
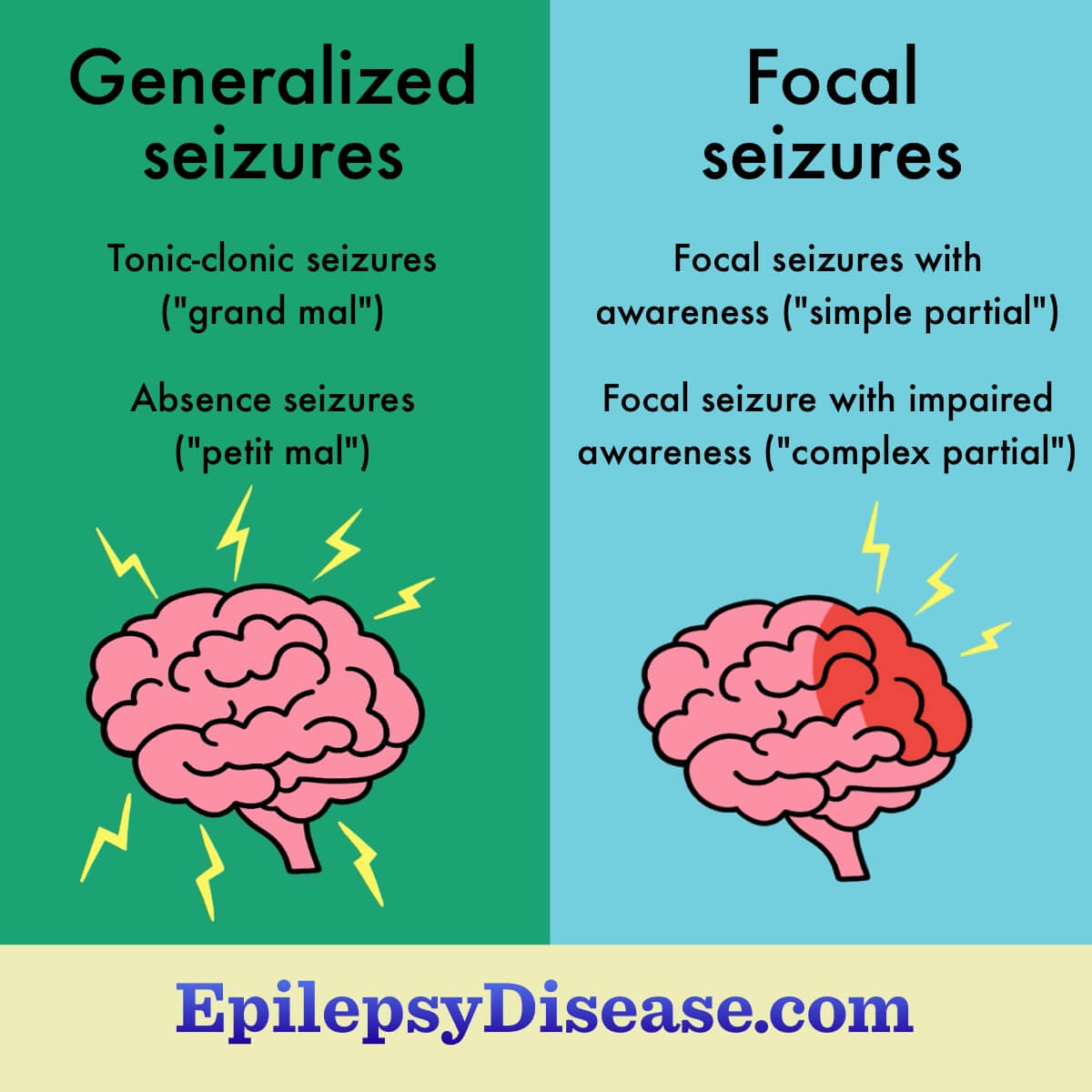
Generalized epilepsy types
Generalized epilepsies are seizures that happen on both sides of the brain. The seizure may also start on 1 side of the brain and spread to the whole brain. People with these type of seizures are usually not aware of their surroundings or lose consciousness.3
There are 2 major types of generalized epilepsy: Generalized tonic-clonic and absence seizures.
Generalized tonic-clonic
"Grand mal" is the old name for this type of epilepsy. These seizures have phases that can last several minutes:2,3
- The person stiffens, loses consciousness, and falls to the floor (tonic phase)
- They then starts jerking violently (clonic phase)
- They then become confused and disoriented (postictal phase)
Injuries from falling, tongue biting, and incontinence are common with these types of seizures. After the seizure, the person is sleepy and confused, and feels weak. It can take seconds to many hours for someone to recover from this type of seizure.3
Absence
"Petit mal" is the old name for this type of epilepsy. Absence epilepsy is named for the blank stare common during these seizures. It is more common in childhood.4
Someone with this type of epilepsy will lose consciousness for a few seconds, then stop what they are doing to stare without expression. This usually lasts for 5 to 10 seconds but can be longer. Seizures may happen several times a day, and in severe cases even hundreds of times a day. After the seizure, the person returns to normal. Someone may also have atypical absence seizures.4
Focal epilepsy types
Focal epilepsy is also called partial or localized epilepsy. Focal seizures are caused by activity on 1 side of the brain, in 1 specific portion of the brain. These are the most common type of seizures. People with these seizures generally remain aware of what is happening.1,2,5
Focal seizures with awareness
These used to be called simple partial seizures. These seizures vary greatly in time and impact. What happens during the seizure depends on the part of the brain in which the seizure occurs. For example, a seizure beginning in the back of the brain (occipital lobe) can cause vision changes. In this case, the person may see flashing lights. A seizure beginning in the hypothalamus can cause uncontrolled laughter. Some people sense when a seizure is about to start. This is called an “aura.” Sometimes people are confused afterward, but not always.
Focal seizure with impaired awareness
This type may also be called a complex partial seizure. This is the most common seizure type in adults with epilepsy. With these seizures, the person may be aware of what is happening in the early part of the seizure then seem "out of it" and lose awareness. They may stare into space and repeat movements, such as smacking their lips, chewing, fidgeting, or walking around.6
These seizures usually last a few minutes, but the time can vary greatly. Some people feel warning signs, called an aura, that a seizure is coming.6
Focal-to-bilateral type
Focal-to-bilateral tonic-clonic seizures include elements of both focal and generalized seizures. This is a seizure that begins on 1 side of the brain and spreads to both sides. How long these seizures last varies widely. It was once called a partial with secondary generalization seizure.7
Unknown onset type
Sometimes the beginning of a seizure is not known or was not witnessed by anyone else. This can happen if seizures take place at night or if the person lives alone. When this happens it may be called an unknown onset seizure.8